Abdominal ultrasound
RDV échographie en ligne sur Doctolib
Prenez rendez-vous pour un échographie dans nos centres
Prise de rendez-vous échographie – Paris 75009
Prise de rendez-vous échographie – Paris 75015
Prise de rendez-vous échographie – Paris 75009 Drouot

Abdominal pain ?
Les douleurs abdominales, souvent aiguës, signalent diverses conditions. Il est primordial de consulter un médecin face à une douleur persistante. Ces douleurs peuvent provenir de diverses sources, notamment du foie ou de la vésicule biliaire, et nécessitent une attention médicale.
Une perte de poids inexpliquée accompagnant ces douleurs est un symptôme préoccupant. Le médecin traitant évaluera les symptômes associés pour diagnostiquer la cause. Les douleurs localisées au niveau de l’estomac peuvent indiquer des cas de maladies spécifiques.
Des conditions telles que le syndrome de l’intestin irritable et les kystes ovariens sont des causes communes de douleurs abdominales. Parfois, une intervention chirurgicale s’impose pour traiter ces affections. Les types de douleurs abdominales varient et chaque type donne des indices sur la cause sous-jacente.
In some cases, an ectopic pregnancy causing severe abdominal pain requires urgent intervention. So it's crucial to recognize these signals and act quickly.
In short, acute abdominal pain should always be taken seriously. Prompt consultation with an attending physician is recommended to avoid complications.
What is an abdominal ultrasound ?
Aabdominal ultrasound consiste à explorer les organes de l’abdomen solides ou contenant du liquide – foie, pancréas, vésicule biliaire, voies biliaires, reins, rate –, les vaisseaux sanguins, etc. Une attention particulière est aussi portée à l’abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava.
Why do I need an abdominal ultrasound?
The world of medical imaging has made significant strides in diagnosing and understanding the human body. As one of these technologies, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) offers detailed images of internal structures without requiring invasive procedures. In this article, we discuss the crucial role of lumbar spine MRI in diagnosing conditions affecting the lower back. abdominal ultrasound can be prescribed for abdominal pain. It can be used to diagnose various pathologies affecting the different organs of the abdomen.
Bien plus, elle est particulièrement réalisée dans le cadre du suivi d’une pathologie.
Last but not least, it can be used to detect and highlight abnormal abdominal masses (lymph node, calculus) and distinguish a solid mass from a liquid mass (e.g. cyst).
What pathologies or anomalies can be detected?
The world of medical imaging has made significant strides in diagnosing and understanding the human body. As one of these technologies, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) offers detailed images of internal structures without requiring invasive procedures. In this article, we discuss the crucial role of lumbar spine MRI in diagnosing conditions affecting the lower back. abdominal ultrasound peut s’avérer déterminante en présence de douleurs abdominales. Ce faisant, elle permet de diagnostiquer diverses pathologies sur les différents organes de l’abdomen, à savoir :
- Calculations at the gall bladder ;
- une cirrhose, une liver steatosisa cysta liver tumor;
- une dilatation ou une obstruction des voies biliaires ;
- une pancréatite, des kystes au niveau du pancréas, une fibrose ;
- une fibrose, une nécrose, une rupture of the spleen ;
- From lymph nodes intra-abdominal (adenopathies) ;
- Vessel thrombosis;
- from kidney stones;a dilated kidney;
- Ascites (presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity).
Ultrasound can also be used to guide biopsies. However, in some cases doppler technique is necessary when performing an ultrasound scan.
Qu’est-ce qu’un écho-Doppler ?
La technique du doppler est un complément à un examen échographique et consiste à enregistrer la vitesse et le sens circulatoire des vaisseaux, selon le principe du sonar. On réalise un Doppler dans le même temps que l’échographie, et ceci ne requiert ni matériel ni préparation spécifique.
Doppler ultrasound helps the physician to see and evaluate :
-
les blocages de la circulation sanguine (tels que les caillots).
-
vessel narrowing
-
tumors and congenital vascular malformations
-
la réduction ou l’absence de flux sanguin vers divers organes, tels que les testicules ou les ovaires.
-
increased blood flow, which may be a sign of infection.
In addition, other procedures can be performed to assess the abdomen, including abdominal x-rays the computer tomography (CT scan) of the abdomen and the abdominal angiography. For example, as the stomach and intestine cannot be studied by ultrasound, it is necessary to turn to CT scan, MRI or fibroscopy.
Pourquoi choisir IMPC pour votre échographie abdominale ?
-
A réseau de 10 centres d’imagerie médicale à Paris.
-
From échographes de dernière génération pour des images haute précision.
-
Des radiologues expérimentés en imagerie abdominale.
-
Rendez-vous rapide en ligne via la page contact ↗.
-
Un accompagnement humain et rassurant.
How is an abdominal ultrasound performed?
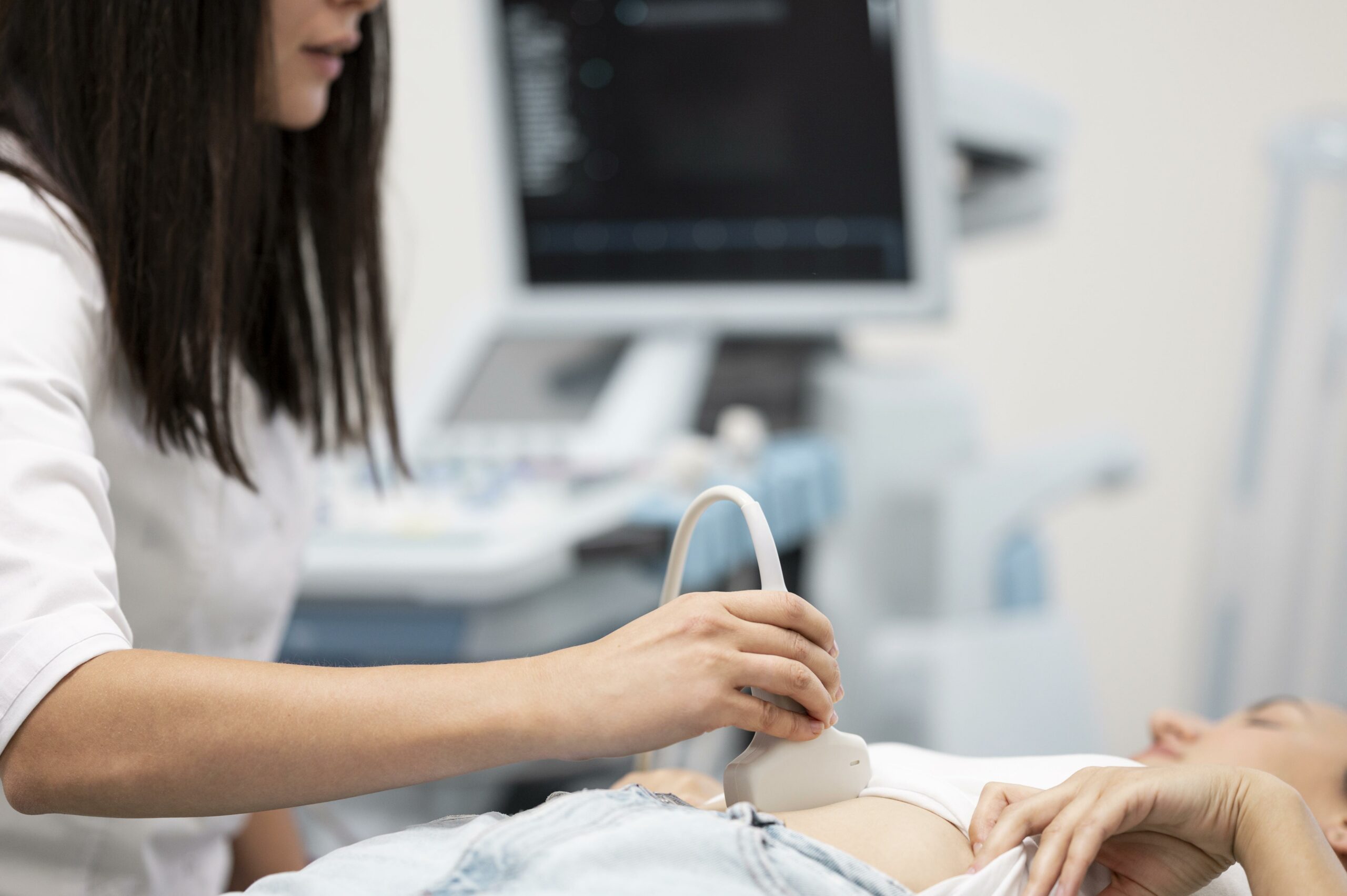
During an abdominal ultrasound scan, the practitioner uses an ultrasound probe to slide over the patient's abdomen. This method is called the transcutaneous route, where the probe passes through the abdominal wall. In some cases, an alternative method is used, the endocavitary route, which involves inserting the probe into the vagina or rectum to get closer to the area to be examined.
Before beginning, the practitioner applies a cool gel to the patient's abdomen. This gel has a crucial function: it facilitates ultrasound transmission from the probe to the internal organs. By moving the probe over the abdomen, the practitioner captures various cross-sectional images of the body's interior. These images appear in real time on a screen connected to the ultrasound machine. This process provides detailed views of internal structures, essential for medical diagnosis.
When should I go to the radiologist?
Toute douleur qui persiste plus de 6 semaines doit interpeller et faire consulter un rhumatologue.
Quels sont les avantages d’une échographie abdominale ?
-
Most ultrasound scans are non-invasive (no needles or injections).
-
Ultrasound imaging is extremely safe and reliable. does not use radiation.
-
Abdominal ultrasound provides clear image of soft tissue that don't show up well on X-ray images.
-
Ultrasound allows real-time imaging. This makes it a good tool for guiding minimally invasive procedures such as needle biopsies and fluid aspiration.
Pour aller plus loin : l’écho-endoscopie, un outil supplémentaire dans le diagnostic des douleurs abdominales.
Abdominal echo-endoscopy is an imaging technique increasingly used to diagnose diseases of the abdomen. It combines the advantages of endoscopy and ultrasound, enabling in-depth exploration of the digestive tract and surrounding structures, including the liver and kidneys. This painless method is particularly effective in detecting abnormalities, such as lesions in the digestive organs or masses in the pelvis. When a radiologist prescribes an echo-endoscopy, he or she is often looking to visualize arteries and organs in order to detect vascular or liver pathologies, but also to assess the condition of the colon and other parts of the digestive system.
The examination is performed using an ultrasound scanner that generates anatomical images in real time. These images can be used to analyze organ structure and identify potential abnormalities, facilitating early diagnosis of serious diseases. If a suspicious lesion is detected, a biopsy can be performed simultaneously, providing tissue samples for histological analysis. This combined approach reduces the need for operative surgical interventions, as it offers a detailed view without the need for invasive procedures. What's more, echo-endoscopy can also be used to guide the physician through targeted interventions, improving the precision of treatment. In short, this technique is an invaluable tool for gastroenterologists and radiologists, enabling them to optimize the detection and diagnosis of abdominal pathologies while minimizing the risk to patients.
FAQ : Les questions les plus fréquentes sur l’échographie abdominale
Faut-il être à jeun pour une échographie abdominale ?
Oui, il est recommandé d’être à jeun 4 à 6 heures avant pour obtenir des images de meilleure qualité.
L’échographie abdominale est-elle douloureuse ?
Non, l’examen est totalement indolore. Seul le gel peut être légèrement froid.
Peut-on faire une échographie abdominale pendant la grossesse ?
Oui, elle est sans danger et même très utilisée pour surveiller la grossesse.
Combien de temps dure l’examen ?
Environ 15 à 20 minutes selon les organes explorés.
Nos spécialistes :
-
Nabil Jomaah
Sources scientifiques
-
Haute Autorité de Santé (HAS) – Guide des examens d’imagerie abdominale (2021).
-
Société Française de Radiologie – Imagerie abdominale et digestive.
-
Inserm – Maladies du foie et diagnostic par échographie (2020).
Dernière mise à jour : le 30 août 2025
Dr Anne Elodie Millischer
